Preface for Teachers
|
|
1. Student Audience and Preparedness
|
|
2. Our Emphasis on Mastery, Integration, and Wonder
|
|
3. Recommendations for Teaching With This Text
|
|
4. Laboratory Work and Lab Reports
|
Preface for Students
|
Introduction: What is Chemistry All About?
|
|
I.1 A Few Major Themes
|
|
I.1.1 Chemistry Is All About Electrons
|
|
I.1.2 Chemistry Is All About Electrical Forces
|
|
Hmm… Interesting. Neon Signs and Photons
|
|
I.1.3 Chemistry Is All About Minimizing Energy
|
|
I.1.4 Chemistry Is All About Whole Number Ratios of Atoms
|
|
I.1.5 Chemistry Is All About Modeling
|
|
I.2 Conclusion
|
|
|
Chapter 1: Atomic Structure
|
|
1.1 Atomic Spectra
|
|
1.1.1 The Electromagnetic Spectrum
|
|
1.1.2 The Energy in Atoms
|
|
Hmm… Interesting. Neon Signs and Photons
|
|
1.1.3 The Hydrogen Atom
|
|
1.2 The Bohr Model of the Atom
|
|
1.3 The Quantum Model of the Atom
|
|
1.3.1 Schrödinger and Pauli
|
|
1.3.2 Shells, Subshells, and Orbitals
|
|
1.3.3 The Aufbau Priciple, the Madelung Rule, and Hund’s Rule
|
|
1.4 Electron Configurations
|
|
1.4.1 Electron Configurations and Orbital Diagrams
|
|
1.4.2 Condensed Electron Configurations
|
|
1.4.3 Anomalous Electron Configurations
|
|
1.5 Isotopes and Atomic Masses
|
|
1.5.1 Isotopes
|
|
1.5.2 The Unified Atomic Mass Unit
|
|
1.5.3 Atomic Masses
|
|
1.5.4 The Mole and the Avogadro Constant
|
|
1.5.5 Molar Mass and Formula Mass
|
|
1.5.6 Gram Masses of Atoms and Molecules
|
|
1.5.7 Percent Composition and Empirical Formulas
|
|
1.5.8 Determining a Molecular Formula from an Empirical Formula
|
|
1.5.9 Significant Digit Rules for Addition
|
|
|
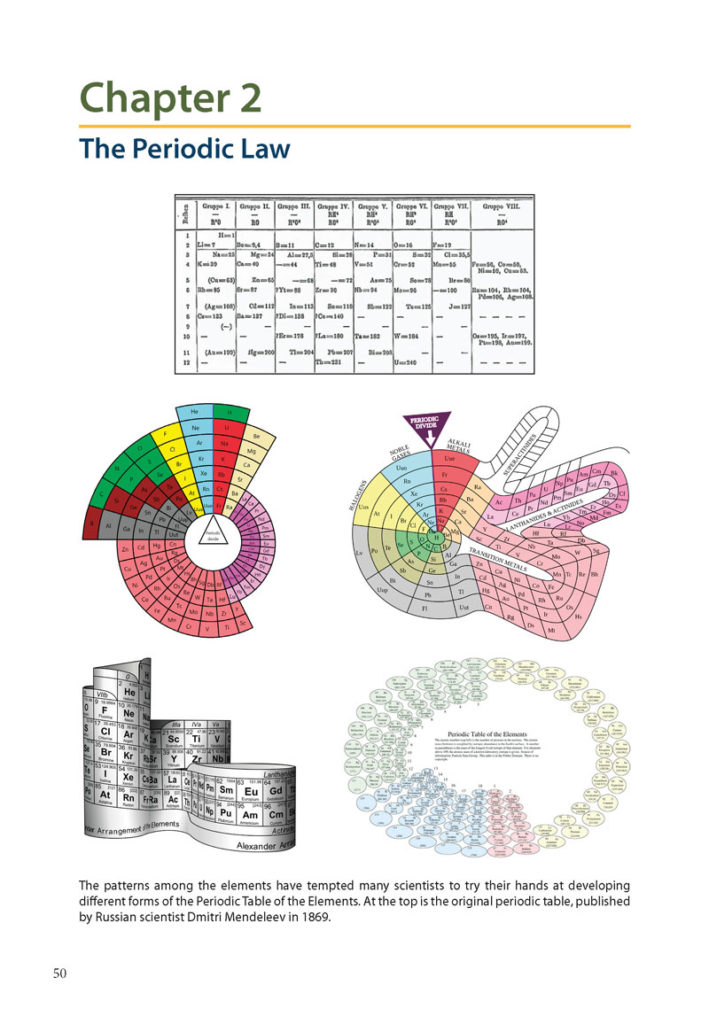
Chapter 2: The Periodic Law
|
|
2.1 The Periodic Table of The Elements
|
|
2.2 Periodic Table Nomenclature
|
|
2.3 Periodic Physical Properties
|
|
2.3.1 Atomic Radius and Bonding Atomic Radius
|
|
2.3.2 Ionic Radius
|
|
2.4 Periodic Chemical properties
|
|
2.4.1 Core and Valence Electrons
|
|
2.4.2 Effective Nuclear Charge
|
|
2.4.3 Ionization Energy
|
|
2.4.4 Electron Affinity
|
|
2.4.5 Electronegativity
|
|
Hmm… Interesting. Hydrogen in space
|
|
2.5 A Few Notes About Hydrogen
|
|
|
Chapter 3: Chemical Bonding
|
|
3.1 Preliminaries
|
|
3.1.1 Types of Substances
|
|
3.1.2 Chemical Possibilities
|
|
3.1.3 The Octet Rule
|
|
3.2 Ionic Bonding
|
|
3.2.1 Ionic Bonds and Crystals
|
|
3.2.2 Naming Ionic Compounds
|
|
3.2.3 Energy in Ionic Bonds
|
|
3.2.4 Hydrates
|
|
3.2.5 Intensive and Extensive Properties
|
|
3.2.6 Physical Properties of Ionically Bonded Substances
|
|
3.3 Covalent Bonding
|
|
3.3.1 Covalent Bonds and Molecules
|
|
3.3.2 Polyatomic Ions
|
|
3.3.3 Ionic Compounds With Polyatomic Ions
|
|
3.3.4 Polyatomic Ion Names
|
|
3.3.5 Naming Acids
|
|
3.3.6 Lewis Structures
|
|
3.3.7 Exceptions to The Octet Rule
|
|
3.3.8 Resonance Structures
|
|
3.3.9 Naming Binary Covalent Compounds
|
|
3.3.10 Energy in Covalent Bonds
|
|
3.3.11 Bond Number
|
|
3.3.12 Physical Properties of Covalently Bonded Substances
|
|
3.4 Electronegativity, Polarity, and Bond Character
|
|
3.4.1 Polarity and Dipoles
|
|
3.4.2 The Nature of The Bond
|
|
Hmm… Interesting. The molecular structure of glass
and quartz
|
|
|
Chapter 4: Molecular Theory and Metallic Bonding
|
|
4.1 Molecular Structure
|
|
4.1.1 Covalent Bond Theory
|
|
4.1.2 Valence Shell Electron Pair Repulsion (VSEPR) Theory
|
|
4.1.3 The Effect of Nonbonding Domains on Bond Angle
|
|
4.1.4 Orbital Hybridization Theory
|
|
4.1.5 Valence-Bond Theory
|
|
4.2 Metallic Bonding
|
|
4.2.1 Metallic Lattices
|
|
Hmm… Interesting. Tin pest
|
|
4.2.2 Physical Properties of Metals
|
|
4.3 Intermolecular Forces
|
|
4.3.1 Bonding Forces
|
|
4.3.2 Intermolecular Forces
|
|
4.3.3 Hydrogen Bonding
|
|
4.3.4 Van Der Waals Forces
|
|
|
Chapter 5: Chemical Reactions and Stoichiometry
|
|
5.1 Introduction to Chemical Equations
|
|
5.1.1 Fascinating Chemistry
|
|
5.1.2 The Law of Conservation of Mass in Chemical Reactions
|
|
5.1.3 Reaction Notation
|
|
5.1.4 Balancing Chemical Equations
|
|
5.1.5 Oxidation States
|
|
Hmm… Interesting. Why nitrates and nitros blow up
|
|
5.2 General Types of Chemical Reactions
|
|
5.2.1 Synthesis Reactions
|
|
5.2.2 Decomposition Reactions
|
|
5.2.3 The Activity Series of Metals
|
|
5.2.4 Single Replacement Reactions
|
|
5.2.5 Double Replacement Reactions
|
|
Hmm… Interesting. A story about aqua regia
|
|
5.2.6 Combustion Reactions
|
|
5.2.7 Acid-Base Reactions
|
|
5.2.8 Oxidation-Reduction Reactions
|
|
5.3 Stoichiometry
|
|
5.3.1 StoichiometricCalculations
|
|
5.3.2 Limiting Reactant
|
|
5.3.3 Theoretical Yield and Percent Yield
|
|
|
Chapter 6: Kinetic Theory and States of Matter
|
|
6.1 Temperature, Kinetic-Molecular Theory, and Pressure
|
|
6.1.1 Temperature and Molecular Energy
|
|
6.1.2 Velocity Distribution of Gases
|
|
6.1.3 The Kinetic-Molecular Theory of Gases
|
|
6.1.4 Gas Pressure
|
|
6.2 States of Matter
|
|
6.2.1 The Four Basic States of Matter
|
|
Hmm… Interesting. How barometers work
|
|
6.2.2 Solids
|
|
6.2.3 Liquids
|
|
6.2.4 Gases
|
|
Hmm… Interesting. Gas diffusion
|
|
6.2.5 Plasmas
|
|
6.2.6 Phase Transitions and Phase Diagrams
|
|
6.2.7 Heat Capacity, Heat of Fusion, and Heat of Vaporization
|
|
6.2.8 Evaporation
|
|
6.2.9 Vapor Pressure
|
|
|
Chapter 7: The Gas Laws
|
|
7.1 Early Formulations of The Gas Laws
|
|
7.1.1 Boyle’s Law
|
|
7.1.2 Charles Law
|
|
7.1.3 Avogadro’s Law
|
|
7.2 The Ideal Gas Law
|
|
7.2.1 Standard Temperature and Pressure
|
|
7.2.2 The Ideal Gas Law
|
|
Hmm… Interesting. The gas laws as models
|
|
7.2.3 Using The Ideal Gas Law to Find Molar Mass and Density
|
|
7.3 The Law of Partial
|
|
7.3.1 Dalton’s Law of Partial Pressures
|
|
7.3.2 Collecting A Gas Over Water
|
|
7.4 Stoichiometry of Gases and Effusion
|
|
7.4.1 Stoichiometry of Gases
|
|
7.4.2 Gas Diffusion and Effusion
|
|
Hmm… Interesting. Uranium enrichment
|
|
|
Chapter 8: Solution Chemistry
|
|
8.1 What Is and Is Not A Solution
|
|
8.1.1 Suspensions
|
|
8.1.2 Colloidal Dispersions
|
|
Hmm… Interesting. Brownian motion
|
|
8.2 Dissolution
|
|
8.2.1 The Process of Dissolving
|
|
8.2.2 Enthalpy of Solution
|
|
8.2.3 Entropy and Free Energy
|
|
8.2.4 Electrolytes
|
|
8.3 Solubility
|
|
8.3.1 Ionic Solids in Water
|
|
8.3.2 Ionic Solids in Nonpolar Solvents
|
|
8.3.3 Polar Liquids
|
|
8.3.4 Nonpolar Liquids
|
|
8.3.5 Solutions of Solids
|
|
Hmm… Interesting. How soap works
|
|
8.3.6 Gases in Liquid Solutions: Le Châtelier’s Principle and Henry’s Law
|
|
8.3.6 The Effect of Temperature on Solubility
|
|
8.4 Quantifying Solution Concentration
|
|
8.4.1 Molarity
|
|
8.4.2 Molality
|
|
8.5 Compounds in Aqueous Solution
|
|
8.5.1 Ionic Equations and Precipitates
|
|
8.5.2 Net Ionic Equations and Spectator Ions
|
|
8.6 Colligative Properties of Solutions
|
|
8.6.1 Vapor Pressure Lowering
|
|
8.6.2 Freezing Point Depression and Boiling Point Elevation
|
|
8.6.3 Osmotic Pressure
|
|
|
Chapter 9: Acids and Bases
|
|
9.1 Properties and Nomenclature of Acids and Bases
|
|
9.1.1 Introduction
|
|
9.1.2 Properties of Acids and Bases
|
|
9.1.3 Acid Names and Formulas
|
|
9.2 Acid-Base Theories
|
|
9.2.1 Arrhenius Acids and Bases
|
|
9.2.2 Brønsted-Lowry Acids and Bases
|
|
Hmm… Interesting. What is an alkali?
|
|
9.2.3 Lewis Acids and Bases
|
|
9.2.4 Strength of Acids and Bases
|
|
9.3 Aqueous Solutions and pH
|
|
9.3.1 The Self-ionization of Water
|
|
9.3.2 Calculating [H3O+] and [OH–]
|
|
9.3.3 pH as a Measure of Ion Concentration and Acidity
|
|
9.3.4 pH Measurement, pH Indicators, and Titration
|
|
9.3.5 Titration Procedure
|
|
9.3.6 Determining [H3O+] or [OH–]
from Titration Data
|
|
|
Chapter 10: Thermochemistry and Kinetics
|
|
10.1 Energy in Chemical Reactions
|
|
10.1.1 Introduction
|
|
10.1.2 Enthalpy
|
|
10.1.3 Understanding Enthalpy and Energy
|
|
10.1.4 Enthalpy of Combustion
|
|
10.1.5 Enthalpy of Formation
|
|
10.2 Calculating Enthalpy of Reaction and Enthalpy of Formation
|
|
10.2.1 Hess’s Law
|
|
10.2.2 Hess’s Law and The General Enthalpy Change Equation
|
|
10.3 Free Energy
|
|
10.3.1 Brief Review of Enthalpy and Entropy
|
|
10.3.2 More on Entropy
|
|
10.3.3 Gibbs Free Energy
|
|
10.4 Reaction Kinetics
|
|
10.4.1 Collision Theory
|
|
10.4.2 Factors Influencing Reaction Rate
|
|
10.4.3 Reaction Mechanisms
|
|
10.4.4 Activation Energy and The Activated Complex
|
|
10.4.5 Reaction Rate Laws
|
|
10.4.6 Rate Laws and Reaction Mechanisms
|
|
|
Chapter 11: Chemical Equilibrium
|
|
11.1 Physical and Chemical Equilibrium
|
|
11.1.1 Equilibria We Have Seen So Far
|
|
Hmm… Interesting. Is dissolution a chemical change?
|
|
11.1.2 Dynamic Chemical Equilibrium
|
|
11.1.3 The Law of Chemical Equilibrium and the Equilibrium Constant
|
|
11.1.4 Le Châtelier’s Principle and Equilibrium Shifts
|
|
11.1.5 Reaction That Go To Completion
|
|
11.1.6 The Common-Ion Effect
|
|
11.2 Acid-Base Equilibrium
|
|
11.2.1 The Acid Dissociation Constant
|
|
11.2.2 The Base Dissociation Constant
|
|
11.2.3 Buffered Solutions
|
|
11.2.4 Hydrolysis of Salts
|
|
Hmm… Interesting. Buffering in blood
|
|
11.3 Solubility Equilibria
|
|
11.3.1 The Solubility Product
|
|
11.3.2 Calculating Ksp From Concentration Or Solubility Data
|
|
11.3.3 Calculating Solubility From Ksp
|
|
11.3.4 Using Ksp to Predict Precipitation
|
|
|
Chapter 12: Redox Chemistry
|
|
12.1 Oxidation and Reduction
|
|
12.1.1 Introduction to Redox Reactions
|
|
12.1.2 Oxidation States
|
|
12.1.3 Strengths of Oxidizing and Reducing Agents
|
|
12.2 Redox Reaction Equations
|
|
12.2.1 Redox Half-Reactions
|
|
12.2.2 Balancing Redox Equations
|
|
12.3 Electrochemistry
|
|
12.3.1 Copper and Zinc Redox
|
|
12.3.2 Electricity Instead of Heat
|
|
12.3 Electrochemistry
|
|
12.3.1 Copper and Zinc Redox
|
|
12.3.2 Electricity Instead of Heat
|
|
12.3.3 Electrochemical Cells
|
|
Hmm… Interesting. How are salt bridges made?
|
|
12.3.4 Electrode Potentials
|
|
12.3.5 Electrochemical Applications
|
|
|
Chapter 13: Organic Chemistry—An Introduction
|
|
13.1 The Chemistry of Carbon
|
|
13.1.1 Introduction
|
|
13.1.2 Carbon Molecular Geometry
|
|
13.1.3 Carbon Allotropes
|
|
13.2 Hydrocarbons
|
|
13.2.1 Alkanes
|
|
Hmm… Interesting. The end of CFCs (almost)
|
|
13.2.2 Alkyl Groups
|
|
13.2.3 IUPAC Naming Standards
|
|
13.2.4 Functional Groups
|
|
13.2.5 Alkenes and Alkynes
|
|
Hmm… Interesting. Fractional distillation
|
|
13.2.6 Carboxylic Acids and Esters
|
|
13.2.7 Aromatic Compounds
|
|
13.3 Compounds Containing Oxygen and Nitrogen
|
|
13.3.1 Alcohols and Ethers
|
|
13.3.2 Aldehydes and Keytones
|
|
13.3.3 Carboxylic Acids and Esters
|
|
13.3.4 Nitrogen Compounds: Amines and Amides
|
|
Hmm… Interesting. Trans fats
|
|
13.4 Polymers
|
|
13.4.1 Types of Polymers
|
|
13.4.2 Polymerization
|
|
13.4.3 A Short Polymer Showcase
|
|
13.5 A Wee Bit of Biochemistry
|
|
Hmm… Interesting. Recycling numbers
|
|
|
Glossary
|
Answers to Selected Exercises
|
Appendix A: Units, Unit Conversions, Significant Digits, and Scientific Notation
|
|
A.1 The SI Unit System
|
|
A.2 Metric Prefixes
|
|
A.3 Converting Units of Measure
|
|
A.4 Converting Temperature Units
|
|
A.5 Accuracy and Precision
|
|
A.6 Significant Digits
|
|
A.7 Scientific Notation
|
Appendix B: Reference Data
|
Appendix C: Scientists to Know About
|
References and Citations
|
Image Credits
|
Index
|
 Accelerated Chemistry is an ideal text for students who love science and aspire to a STEM-oriented college program. This book contains up-to-date chemistry information, beautiful illustrations, and lucid narrative. It also supports Novare’s trademark mastery-learning paradigm.
Accelerated Chemistry is an ideal text for students who love science and aspire to a STEM-oriented college program. This book contains up-to-date chemistry information, beautiful illustrations, and lucid narrative. It also supports Novare’s trademark mastery-learning paradigm. As with all Centripetal Press textbooks, our design philosophy guides the layout and composition of the text. Colors and images are attractive without being distracting. Our books are designed to be read and studied, and the presentation as well as the voice of the narrator supports that.
As with all Centripetal Press textbooks, our design philosophy guides the layout and composition of the text. Colors and images are attractive without being distracting. Our books are designed to be read and studied, and the presentation as well as the voice of the narrator supports that.